Honeycomb / Flat Wire conveyor Belt
HOME / PRODUCTS / Metal Conveyor Belts / Honeycomb / Flat Wire Conveyor Belts
Honeycomb / Flat Wire Belt is a type of durable metal mesh belt for tough industrial conveying
Flat wire belts, also referred to as honeycomb conveyor belts, stands out as a distinctive type of conveyor belt distinguished by its level carrying surface and a structural configuration resembling a honeycomb.
The key elements and features of flat wire belts include flat wire strips and cross rods. The Flat wire strips, forms a grid-like pattern, establishing a flat and stable surface crucial for applications demanding even and steady conveying. The cross rods connect the flat wire strips horizontally, enhancing structural integrity, maintaining proper spacing, and ensuring alignment. These cross rods play a pivotal role in bolstering the overall strength and durability of the belt.
Specification
| Cross rod pitch: | 12.7 – 50.8 mm |
| Flat wire pitch: | 12.7 – 40.0 mm |
| Cross rod diameter: | 2.5 – 8.0 mm |
| Strip section dimensions: | 9.5 x 1.2 – 12.5 x 2.0 mm |
| Standard materials: | common black steel, galvanized steel, stainless steel |
| Belt width: | 200 mm to 5,000 mm. |
| Working temperature: | up to 400°C |
| Edging: | Welded ege, clinched edge, chain edge |
Belt Types
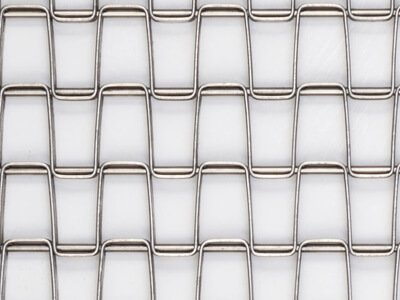

Standard Weight Flat Wire Belts
For standard weight flat wire belts, 1/2" x 1/2", 1/2" x 1", 1" x 1", 1/2" x 1" are frequently used, and other special specifications are available on request.
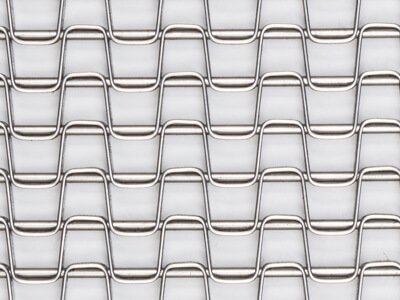

Heavy Duty Flat Wire Belts
The heavy-duty flat wire belts share all the characteristics of standard duty belts, differing only in the incorporation of heavier cross rods and thicker flat strips. With a flat strip measuring 1/2" in width and 0.062" in thickness, coupled with a robust 6-gauge connector rod, this variant boasts approximately 2.5 times the strength of its standard counterpart.
Standard duty is sufficient for most applications, whereas Heavy Duty provides extra long life, heavy load capacity and for tougher conditions.
Edge Availability


Welded Edge Flat Wire Conveyor Belts
Welded edges entail the fusion or welding of the connecting rods at the belt's edges, creating a strong and rigid perimeter. Offers enhanced structural integrity and durability, making it ideal for applications with heavy loads or operating in demanding industrial environments.


Clinched Edge Flat Wire Conveyor Belts
Clinched edges involve the interlocking of the connecting rods at the belt's edges without welding. The edges are folded over, creating a smooth and continuous surface. Provides a seamless and snag-free conveying surface, making it suitable for applications involving delicate or sensitive products.


Chain Edge Flat Wire Conveyor Belts
Chain edges involve the use of a chain-like configuration along the edges of the belt. This edge type is commonly used for positive drive applications where sprockets engage with the chain, propelling the belt forward.
Methods of Drive
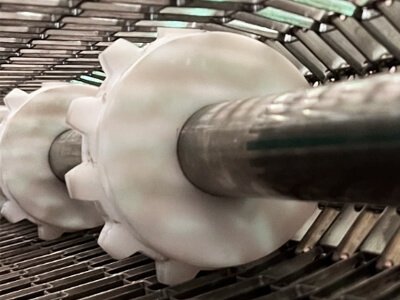

Positive Drive Flat Wire Belts
Positive drive systems involve using sprockets to engage with the mesh of the flat wire belt, providing a positive and synchronized movement. Offers precise control and synchronization, making it suitable for applications where accurate product positioning and movement are critical. Positive drive systems are often used in applications with inclined conveyors or where the belt must positively engage with the sprockets.
Common Specifications of Flat Wire Belts
| Specification Coding | Flat wire pitch (mm) | Cross rod pitch (mm) | Cross rod diameter (mm) | Strip section dimensions (mm) |
| 24.0 – 27.3 – 5.0 – (1.5×12.7) | 24 | 27.3 | 5 | 1.5×12.7 |
| 18.0 – 27.4 – 5.0 – (1.5×12.7) | 18 | 27.4 | 5 | 1.5×12.7 |
| 12.7 – 25.4 – 5.0 – (1.5×12.7) | 12.7 | 25.4 | 5 | 1.5×12.7 |
| 12,7 – 25.4 – 5.0 – (1.5×14.1) | 12.7 | 25.4 | 5 | 1.5×14.1 |
| 25.4 – 25.4 – 5.0 – (1.2×14.1) | 25.4 | 25.4 | 5 | 1.2×14.1 |
| 12.7 – 25.4 – 5.0 – (1.2×14.1) | 12.7 | 25.4 | 5 | 1.2×14.1 |
| 14.0 – 19.05 – 4.0 – (1.2×12.0) | 14 | 19.05 | 4 | 1.2×12.0 |
| 24.0 – 27.3 – 3.0 – (1.2×9.5) | 24 | 27.3 | 3 | 1.2×9.5 |
| 16.0 – 27.4 – 3.0 – (1.2×9.5) | 16 | 27.4 | 3 | 1.2×9.5 |
| 15.0 – 27.0 – 3.0 – (1.2×14.1) | 15 | 27 | 3 | 1.2×14.1 |
| 14.0 – 13.7 – 3.0 – (1.2×9.5) | 14 | 13.7 | 3 | 1.2×9.5 |
| 24.0 – 27.3 – 5.0 – (1.5×12.7) | 24 | 27.3 | 5 | 1.5×12.7 |
| 24.0 – 27.3 – 5.0 – (1.5×12.7) | 24 | 27.3 | 5 | 1.5×12.7 |
| 18.0 – 27.4 – 5.0 – (1.5×12.7) | 18 | 27.4 | 5 | 1.5×12.7 |
Material Availability
The selection of materials for various applications depends on factors such as cost, temperature requirements, corrosion resistance, and abrasion resistance.
1. Galvanized C-1015 Low Carbon Steel:
Advantages:
– Low cost.
– Some rust resistance.
– Operates in temperatures up to 260 ℃.
Considerations:
– Galvanized flaking may occur at temperatures as low as 180 ℃.
– May not be suitable for high-temperature or corrosive environments.
2. High Carbon Steel C-1045:
Advantages:
– Suitable for temperatures ranging from 180 ℃ to 430 ℃.
– Greater abrasion resistance compared to galvanized low carbon steel.
Considerations:
– May not be as corrosion-resistant as stainless steel.
– High carbon steel can be more susceptible to corrosion in certain environments.
3. 304 Stainless Steel:
Advantages
– Suitable for temperatures up to 600 ℃.
– Generally good corrosion resistance.
Considerations:
– Corrosive resistance may start to decline at temperatures around 430 ℃.
– May not be as abrasion-resistant as high carbon steel.
4. 316 Stainless Steel:
Advantages:
– More resistant than 304 stainless steel in sulfuric, acetic, and phosphoric acids.
– Greater overall corrosion resistance compared to 304 stainless steel.
Considerations:
– Suitable for temperatures up to 600 ℃.
– While offering improved corrosion resistance, it may still be affected by certain corrosive environments.
In summary, the choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application. Galvanized low carbon steel may be suitable for low-cost applications with moderate temperature and corrosion requirements. High carbon steel provides greater abrasion resistance but may be more susceptible to corrosion. Stainless steel, particularly 316, offers excellent corrosion resistance but may have limitations in very high-temperature or highly corrosive environments. The selection should be based on a careful consideration of the specific operating conditions and performance criteria.
Flat wire belts, also known as honeycomb conveyor belts, offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in various industrial applications. Here are some key advantages of flat wire belts:
Flat Carrying Surface:
The flat wire strips create a level and stable surface for conveying products. This is essential for applications where an even surface is required for the movement of materials.
Open Mesh Construction:
Flat wire belts the open mesh design allows for quick drainage and facilitates free air circulation. This is particularly beneficial in processes such as washing, drying, cooling, and heating where effective airflow and drainage are essential.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio:
The use of materials like stainless steel in the construction of flat wire belts provides a high strength-to-weight ratio. This makes the belt durable and robust while remaining lightweight, contributing to energy efficiency in conveyor systems.
Versatility in Applications:
Flat wire belts finds applications in a wide range of industries, including transportation, cooking, heating, drying, cooling, drainage, freezing, baking, washing, weed clearing, turf cutting, sorting, recycling, elevating, de-elevating, loading, harvesting, canning, pasteurization, painting, assembly, and proofing.
Ease of Cleaning:
The flat surface and open mesh construction make flat wire belts easy to clean. This is crucial, especially in industries such as food processing, where hygiene and sanitation standards are high.
Easily Joined:
Flat wire belts can be easily joined, simplifying the installation and maintenance processes. This feature adds to the overall efficiency and convenience of using these belts in industrial settings.
Long Service Life:
The durable materials and robust construction contribute to the long service life of flat wire beltis. This results in reduced downtime and maintenance costs, making it a cost-effective choice over the long term.
Positive Tracking:
The positive sprocket drive system ensures that the belt maintains proper tracking, reducing the likelihood of misalignment and enhancing overall system efficiency.
Honeycomb conveyor belts, finds applications in a variety of industries due to its unique design and advantageous features. It is available in a wide variety of aperture configurations to suit applications as diverse as casting, baking, drainage and packaging.
Cooking:
The flat and open design of the belt makes it suitable for cooking applications, such as conveying food items through ovens or grills.
Drying:
Flat wire belting is ideal for applications that involve drying processes, such as conveying wet or damp products through drying systems.
Cooling:
The open mesh construction facilitates air circulation, making flat wire belting suitable for applications that require cooling, such as conveying hot products through cooling zones.
Baking:
The flat and level surface of the belt makes it suitable for conveying products through baking ovens in the food industry.
Washing:
Flat wire belting’s open mesh design allows water to pass through easily, making it suitable for washing applications where cleanliness is crucial.
Weed Clearing:
The belt can be used in agriculture for conveying and clearing weeds or unwanted vegetation.
Turf Cutting:
In landscaping and turf management, flat wire belting may be used for conveying and cutting turf.
Packaging:
Flat wire belting is used in packaging applications where products need to be conveyed through various stages of the packaging process.
Sorting:
The stable and level surface of the belt makes it suitable for sorting applications, where products are moved and sorted based on specific criteria.
Recycling:
Flat wire belting can be used in recycling facilities for conveying and sorting recyclable materials.
Elevating and De-Elevating:
The positive sprocket drive system allows for reliable and controlled movement, making flat wire belting suitable for elevating and de-elevating applications.
Loading and Harvesting:
ndustries such as agriculture and mining may use flat wire belting for loading and harvesting operations.
Canning and Pasteurization:
In the food and beverage industry, flat wire belting can be employed for conveying products through canning and pasteurization processes.









